[Python] Dictionary를 합치는 방법
Python의 dictionary를 합치는 다양한 방법을 살펴봅니다.
개요
안녕하세요.
이번 글에서는 Python의 dictionary를 합치는 다양한 방법에 대해 살펴보겠습니다.
딕셔너리의 결합과 주먹구구식 코드
필요성을 느꼈을 때
다음과 같은 딕셔너리를 다루는 일이 생겼습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
dict_survey = {
...
"hobby":[
None,
{
"영화감상": 2,
},
None,
{
"독서": 4,
},
{
"": 5,
},
None,
None
]
...
}
저는 dict_hobby라는 딕셔너리에 모든 결과값을 넣고 싶었습니다.
그래서 빠르게 코드를 작성하기 시작했습니다.
주먹구구식 코드
가장 처음 작성한 코드는 다음과 같았습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
dict_hobby = dict()
for dict_each in dict_survey["hobby"]:
if dict_each != None:
for k, v in dict_each.items():
dict_hobby[k] = v
하지만 딕셔너리를 합치는 더 좋은 방법이 있지 않을까 생각이 들었고 여러 경로를 찾아보기 시작했습니다.
딕셔너리를 합치는 몇 가지 방법
① dictionary unpacking
1
2
3
4
5
dict_hobby = dict()
for dict_each in dict_survey["hobby"]:
if dict_each != None:
dict_hobby = {**dict_hobby, **dict_each}
딕셔너리의 unpacking을 활용한 방법입니다.
하지만 직관적으로 어떤 역할을 하는지 확인하기 어렵습니다.
② dictionary unpacking2
1
2
3
4
5
dict_hobby = dict()
for dict_each in dict_survey["hobby"]:
if dict_each != None:
dict_hobby = dict(dict_hobby, **dict_each)
딕셔너리의 unpacking을 활용한 두번째 방법입니다.
이전에 비해 직관성을 챙겼습니다.
하지만 이 방법은 딕셔너리의 모든 key가 string일 때만 유효합니다.
③ dict.update
1
2
3
4
5
dict_hobby = dict()
for dict_each in dict_survey["hobby"]:
if dict_each != None:
dict_hobby.update(dict_each)
update 메소드를 사용한 방법입니다.
기본적으로 제공해주는 메소드답게 어떤 역할인지 빠르게 확인 가능합니다.
④ dict union operator ‘|’
1
2
3
4
5
dict_hobby = dict()
for dict_each in dict_survey["hobby"]:
if dict_each != None:
dict_hobby |= dict_each
마지막으로 python 3.9에서 추가된 | 연산자를 활용한 방법입니다.
내부적으로는 update 메소드를 활용한 다음의 코드가 동작합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
...
def __or__(self, other):
if not isinstance(other, dict):
return NotImplemented
new = dict(self)
new.update(other)
return new
def __ror__(self, other):
if not isinstance(other, dict):
return NotImplemented
new = dict(other)
new.update(self)
return new
def __ior__(self, other):
dict.update(self, other)
return self
...
참고로 위의 3가지 메소드는 각각 다음의 연산과 같습니다.
1
2
3
def __or__(a, b) <-> a | b
def __ror__(a, b) <-> b | a
def __ior__(a, b) <-> a |= b
⑤ 실제로 사용한 코드
그렇다면 실제로 사용한 코드는 무엇일까요?
다음의 코드를 사용하였습니다 :)
1
2
3
4
from functools import reduce
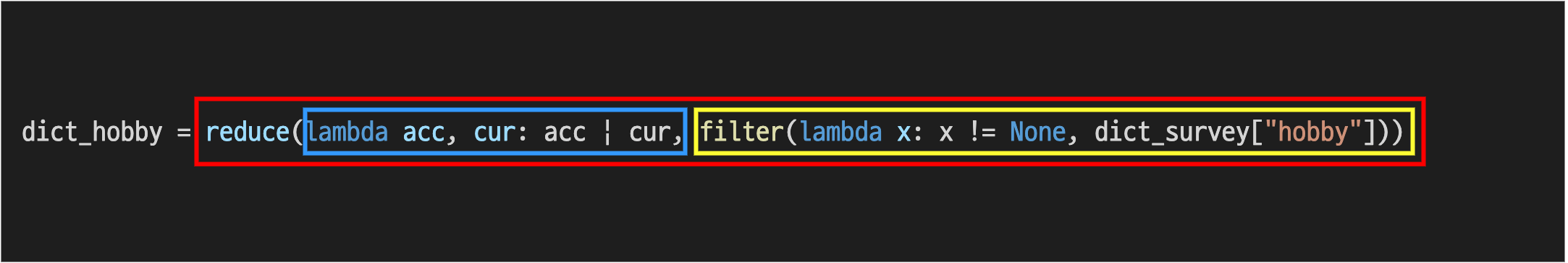
dict_hobby = reduce(lambda acc, cur: acc | cur, filter(lambda x: x != None, dict_survey["hobby"]))
functools의 reduce 함수와 filter 함수를 활용하여 반복문 없이 하나로 합쳐진 딕셔너리를 만들었습니다.
빨간 박스인 reduce 함수는 크게 파란 박스의 function과 노란 박스의 iterable이 필요합니다.
파란 박스인 function에서는 lambda 표현식을 활용하여 acc(누적된 딕셔너리)와 cur(현재 딕셔너리)를 | 연산자로 합칩니다.
노란 박스인 iterable에서는 filter 함수를 통해 None 값을 필터링한 dict_survey["hobby"]를 넘겨줍니다.
마무리하며
이 글에서는 파이썬의 딕셔너리를 합치는 방법에 대해 살펴보았습니다.
기존에는 파이썬의 버전에 따라 어떤 기능이 추가되는지 몰랐지만 이번 기회를 통해 PEP 문서를 살펴보면서 관심을 가지게 되었습니다.
조언과 댓글은 언제나 환영입니다.
감사합니다. 😀
참고 문헌
- PEP 584 – Add Union Operators To dict , https://peps.python.org/pep-0584/
- operator — 함수로서의 표준 연산자, https://docs.python.org/ko/3.11/library/operator.html
- functools — 고차 함수와 콜러블 객체에 대한 연산, https://docs.python.org/ko/3.11/library/functools.html?functools.reduce#functools.reduce
- 내장 함수, https://docs.python.org/ko/3.11/library/functions.html?highlight=filter#filter
- 표현식, https://docs.python.org/ko/3.11/reference/expressions.html?highlight=lambda#lambda